Summer is here and the sun is shinning. Time to grab your towel and sun tanning block and bask in the glorious sun. But before you start gearing up to soak in the sun rays, there's one thing we need to discuss about about our beloved blazing ball of fire in the sky. Those beautiful, bright rays of sun energy emit what is called ultraviolet (UV) radiation. As humans, we need to remind ourselves the skin is a vulnerable organ that needs daily protection. This blog post will help to understand how the sun can negatively impact your skin and, therefore, how to protect your skin from future sun damage.
If you've ever experienced blisters, red tenderness, brown spots appearing on you skin, or that random burning sensation on your back while taking a shower after a few hours in direct sunlight, then you my friend have felt the effects of ultraviolet radiation.
One of the most significant factors affecting skin health is unprotected exposure to the sun. Protecting the skin from UV damage is not just about preventing sunburn; it’s a crucial aspect of long-term skin care that can prevent premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and skin cancer.
What is Ultraviolet Radiation?
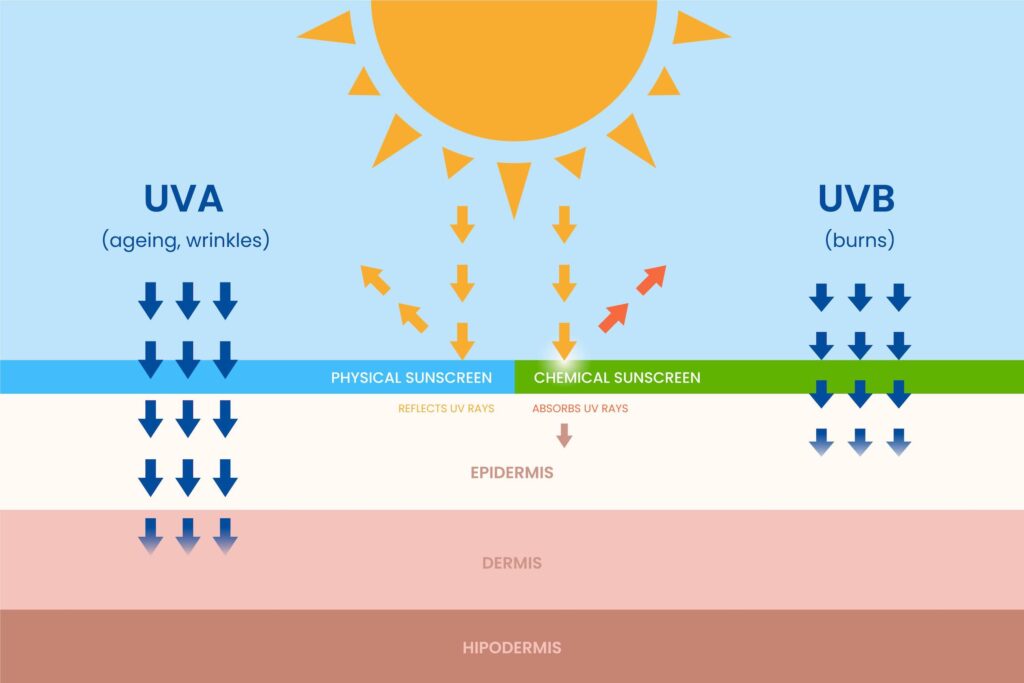
Ultraviolet radiation is a light wave in the form of electromagnetic energy emitted by the sun. The sun is our primary source of natural ultraviolet radiation. Some artificial UV rays are emitted from tanning beds, which are not recommend to use. On the electromagnetic spectrum these waves lie between x-rays and visible light. It has a higher frequency and longer wavelength than the light waves we see. It is classified into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
- UVA (320-400 nm): UVA rays penetrate the skin more deeply entering into the dermis of the skin than UVB and are responsible for immediate tanning and skin aging. UVA rays breakdown DNA and collagen in the dermis which can lead to early aging. They can pass through glass and clouds, making protection necessary even on overcast days and indoors near windows.
- UVB (290-320 nm): UVB rays affect the outer layer or the epidermis of the skin and are the primary cause of sunburn. UVB rays tan the skin by increasing the production of melanin in melanocytes. They play a crucial role in the development of most skin cancers and are most intense between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- UVC (100-290 nm): UVC rays are the most dangerous but are mostly absorbed by the Earth's ozone layer and do not reach the ground, therefore, not affecting the skin.
Why Do You need to Protect Your Skin from the sun?
- Skin Cancer: UV radiation is a well-established risk factor for all major types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that approximately 90% of non-melanoma skin cancers and 86% of melanomas are associated with exposure to UV radiation.
- Premature Aging (Photoaging): Chronic exposure to UVA and UVB rays accelerates the skin aging process. UV radiation breaks down collagen and impairs the skin’s elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and a leathery texture. Studies show that up to 80% of visible aging signs are attributable to sun exposure.
- Hyperpigmentation: UV exposure stimulates melanin production, leading to an uneven skin tone and dark spots. Conditions like melasma and solar lentigines (age spots) are exacerbated by UV radiation.
- Immune Suppression: UV radiation can suppress the local immune response in the skin, reducing its ability to combat infections and contributing to the reactivation of latent viruses like herpes simplex.
How to protect your skin from The SUn?
1. Use Sunscreen Daily:
- Choose Broad-Spectrum SPF: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays. The SPF number indicates the level of protection against UVB rays.
- Apply Generously: Apply at least a teaspoon of sunscreen to your face and a shot glass amount to your body. Don't forget often-missed spots like the ears, neck, and the tops of your feet.
- Reapply Regularly: Reapply every two hours, or immediately after swimming or sweating. Water-resistant sunscreens are beneficial for prolonged outdoor activities.
2. Use Protective Clothing:
- Wear UPF Clothing: Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) clothing offers a fabric-based barrier to UV rays. Look for clothing with a UPF rating of 30 or higher.
- Hats and Sunglasses: A wide-brimmed hat can shade your face, neck, and ears. Sunglasses with UV protection guard your eyes and the delicate skin around them from UVA and UVB rays.
3. Seek Shade:
- Whenever possible, stay in the shade, especially during peak UV radiation hours (10 AM to 4 PM). Use umbrellas or portable canopies when shade is not easily accessible.
4. Avoid Tanning Beds:
- Tanning beds emit UV radiation that can be stronger than the sun. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies tanning devices as carcinogenic to humans.
5. Include Antioxidant-Rich Skincare:
- Topical Antioxidants: Incorporate serums and creams with antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and ferulic acid. These compounds neutralize free radicals generated by UV exposure and enhance the efficacy of sunscreens.
- Dietary Antioxidants: Consume a diet rich in antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds to support your skin from within.
6. Get Regular Skin Checks:
- Self-Examinations: Conduct monthly self-examinations to check for new or changing moles and spots. The ABCDEs of melanoma (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolution) can guide you in identifying suspicious lesions.
- Professional Screenings: Visit a dermatologist annually for a professional skin exam. Early detection of skin changes is critical for effective treatment.
Block The Sun, Not The Fun!
You can't run away from the sun, but you can protect your skin from the sun more efficiently to prevent sunburns, hyperpigmentation and skin cancers. Sunscreen formulations, such as mineral sunscreens with micronized zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, offer non-irritating and highly effective options for broad spectrum UV protection. It's important to note that the sun is yearlong and ultraviolet radiation will penetrate through the atmosphere whether it's a sunny or cloudy day, so as a sign off: ALWAYS WEAR YOUR SUNSCREEN!